Absorbance Definition Biology . absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. L = the length of the light's path through the. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. It is also known as optical density, extinction,.
from www.vedantu.com
L = the length of the light's path through the. Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution.
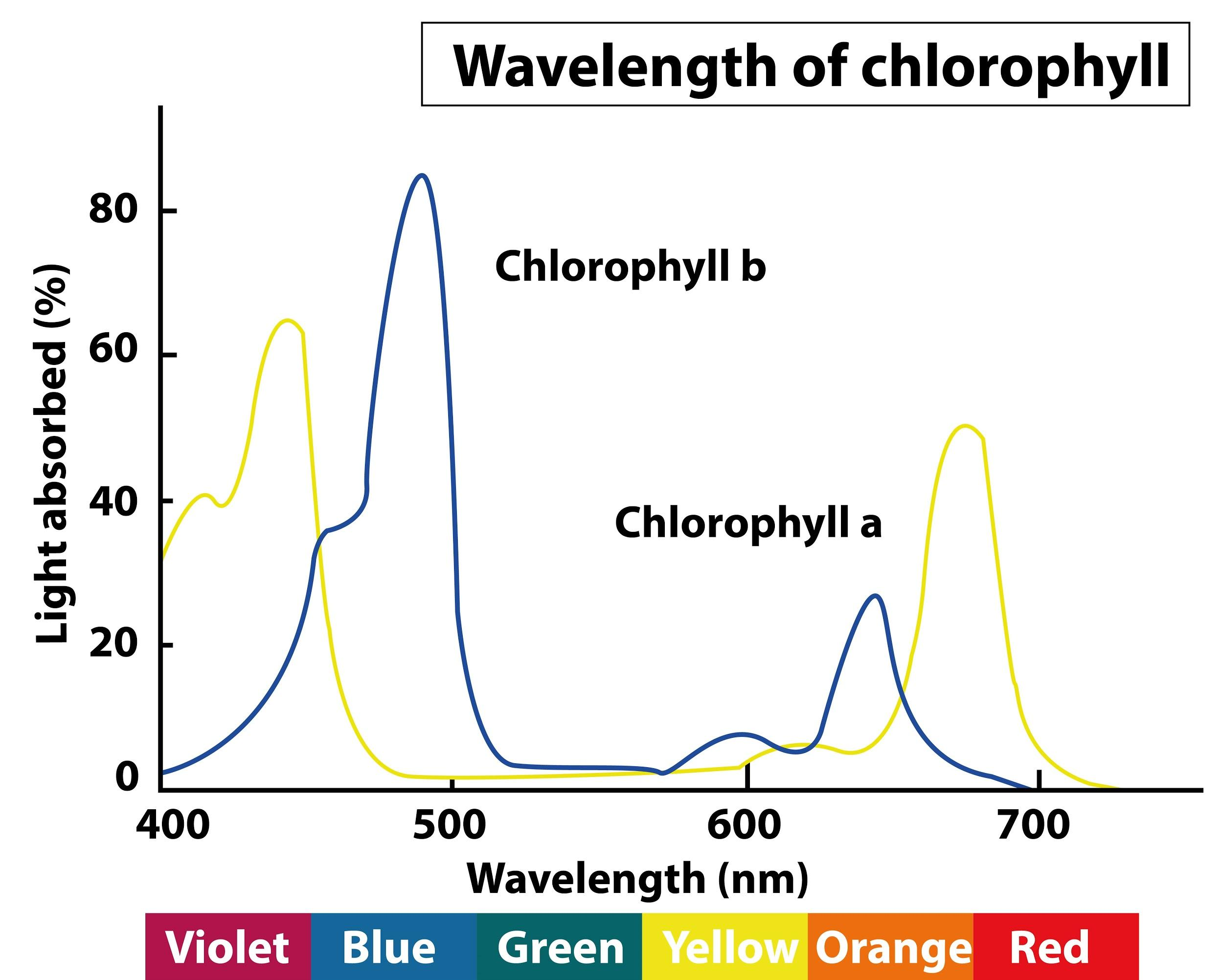
Chlorophylls absorbs visible light of wavelength(a) 400 500 nm only(b
Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. L = the length of the light's path through the. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample.
From www.alamy.com
Absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a and b Stock Photo Alamy Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. L. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Spectroscopy of Proteins PowerPoint Presentation ID6052251 Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. L = the length of the light's path through the. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Normalised (A) absorption and (B) emission spectra of the fluorescent Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. L = the length of the light's path through the. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale.. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Absorbancetime graph of oxidation of streptomycin with mixture of Absorbance Definition Biology Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. L = the length of the. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Variation in a absorbance, b transmittance and c reflectance derived by Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
The normalized absorbance and fluorescence of solutions Absorbance Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Calibration curve of absorbance versus concentration. Download Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. It is also known as optical density, extinction,.. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Absorbance spectra of pigment extraction form ten different biological Absorbance Definition Biology Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; L = the length of the light's path through the. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
Diversity of biological pigment absorbance profiles in the context of Absorbance Definition Biology in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance is directly proportional to the. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.difference.wiki
Molar Absorptivity vs. Specific Absorbance What’s the Difference? Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. L = the length of the light's path through the. absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; absorbance is. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED The absorbance of a molecule in solution A is proportional to Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Absorption Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. in. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Electronic Spectroscopy PowerPoint Presentation, free download Absorbance Definition Biology L = the length of the light's path through the. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.vedantu.com
Chlorophylls absorbs visible light of wavelength(a) 400 500 nm only(b Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. absorbance is directly proportional. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.youtube.com
Transmittance and Absorbance YouTube Absorbance Definition Biology Most spectroscopic phenomena arise from the interaction of a molecule with one photon at a time. in which a = absorbance, the percent of light absorbed; Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. It is also. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From in.pinterest.com
ds or ss DNA has more absorbance?simplified concept graph. Hyperchromic Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. L = the length. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.chemeurope.com
Measuring DNA Absorbance with the STSUV Microspectrometer DNA Absorbance Definition Biology Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. (analytical chemistry) a logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at. It is also known as optical density, extinction,. absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. L = the length of the light's path through the.. Absorbance Definition Biology.
From www.youtube.com
Absorptivity Specific absorbance and Molar absorptivity YouTube Absorbance Definition Biology absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the molecules and is measured on a logarithmic scale. L = the length of the light's path through the. Absorption is the process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs. absorbance (a), also known as optical density (od), is the quantity of light absorbed by. Absorbance Definition Biology.